「朝の血糖が高いのは、インスリンが足りないから?」…実はそれ、インスリンを減らすべきサインかもしれません。
このページでは、「暁現象」と「ソモジー効果」という2つの異なる原因をわかりやすく解説します。

暁現象とは?
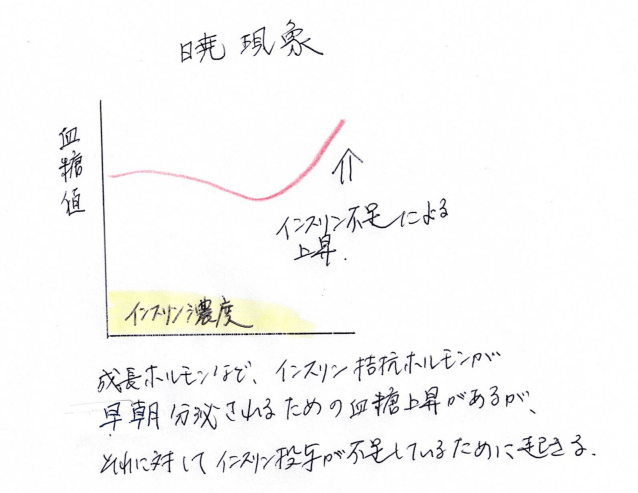
暁現象(Dawn phenomenon)は、早朝4〜6時頃に成長ホルモンやコルチゾールなどのホルモンが分泌され、インスリンの効きが悪くなり、血糖値が自然に上昇する現象です。起床時に血糖が高くなります。
ソモジー効果とは?
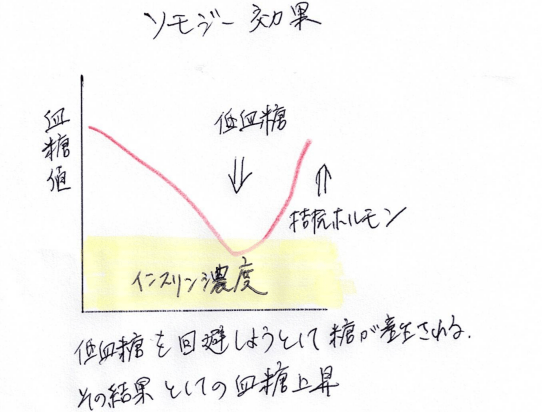
ソモジー効果(Somogyi effect)は、主にインスリン治療中の糖尿病患者に見られる現象で、夜間の低血糖に反応して、体がアドレナリンやグルカゴンを分泌し、その反動で高血糖を起こす状態です。原因は「夜のインスリンが多すぎること」です。発見者であるアメリカの医師、マイケル・ソモジー氏の名にちなんで名付けられました。
ソモジー効果の最も一般的な原因は、インスリン、特に就寝前に投与する中間型や持効型インスリンの量が多すぎることです。その他、以下のような要因も引き金となり得ます。
-
- 夕食の量が少なかった、あるいは炭水化物の摂取が不足していた
- 就寝前の運動量が多かった
- アルコールの摂取
ソモジー効果が起きている場合、夜間に自覚のない低血糖を起こしている可能性があります。以下のような症状が見られることがあります。
-
- 悪夢を見る
- 寝汗をかく
- 朝起きた時に頭痛やだるさを感じる
朝の血糖値が高い場合にソモジー効果を疑うには、夜中の3時頃に血糖値を測定することが有効です。この時間帯に血糖値が低ければ(一般的に70mg/dL未満)、ソモジー効果の可能性が高いと考えられます。
出典:日本糖尿病学会「糖尿病診療ガイドライン2019」p.97–98、糖尿病治療ガイド2022–2023 p.79–80、UpToDate(2024)
違いを見極めるには?
最大の違いは、先行する低血糖の有無です。暁現象では夜中の3時頃に低血糖は見られません。この違いを見極めることが、適切な対処のために非常に重要です。見た目は似ていますが、原因は正反対です。暁現象では「インスリン不足」、ソモジー効果では「インスリン過剰」です。深夜(2〜3時頃)の血糖値を測定することで見極めが可能です。
| 項目 | ソモジー効果 | 暁現象 |
|---|---|---|
| 夜間(深夜2〜3時頃)の血糖 | 低い(低血糖) | 高めまたは変化なし |
| 原因 | 夜間のインスリン過剰 → 低血糖 → 反動で高血糖 | 成長ホルモンやコルチゾールによるインスリン抵抗性 |
| 早朝の血糖 | 高い | 高い |
| 見極め方 | 深夜(2〜3時)の血糖を測定し低ければソモジーを疑う | 深夜に血糖が高めであれば暁現象を疑う |
| 対処法 | 夜間インスリンの減量、就寝前の補食 | 夜間インスリンの増量または種類変更 |
出典:日本糖尿病学会編「糖尿病診療ガイドライン2019」p.97、UpToDate(2024)を参考に筆者作成
対応法の違い
-
-
- 暁現象 → 夜のインスリン量を増やす/超持効型インスリンを使用
- ソモジー効果 → 夜のインスリンを減らす/就寝前の補食をとる
ソモジー効果が疑われる場合、自己判断でインスリン量を調整するのは危険です。必ず医師に相談してください。一般的な対処法としては、以下のようなものが挙げられます。インスリン量の調整: 主治医の指導のもと、原因となっているインスリンの量を慎重に減らします。高血糖だからといってインスリンを増やすと、さらに低血糖を助長し、悪循環に陥るため注意が必要です。
食事内容の見直し: 就寝前に適量の炭水化物を含む補食をとることで、夜間の低血糖を防ぐことができる場合があります。
血糖値のモニタリング: 夜間を含めた血糖値の変動を詳しく把握し、治療方針の決定に役立てます。
ソモジー効果は、良かれと思って行っているインスリン治療が裏目に出てしまう現象です。朝の高血糖が続く場合は、その背景に隠れた低血糖がないかを確認することが、適切な血糖コントロールへの第一歩となります。 -
CGM(持続血糖モニタリング)で可視化
FreestyleリブレやDexcom G7などのCGMを使えば、夜間の血糖変化を正確に把握できます。「夜中の血糖が低くなっているか」を調べるには非常に有効です。
047-467-5500 に電話する
👨⚕️ この記事の監修医師
しもやま内科 院長
日本内科学会 総合内科専門医
日本糖尿病学会 糖尿病専門医・指導医
日本循環器学会 循環器専門医
日本老年医学会 老年病専門医・指導医
日本甲状腺学会 甲状腺専門医
糖尿病、甲状腺、副腎など内分泌疾患の診療に長年従事し、地域密着型の総合内科医として診療を行っています。
